341. 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器
给定一个嵌套的整型列表。设计一个迭代器,使其能够遍历这个整型列表中的所有整数。
列表中的项或者为一个整数,或者是另一个列表。
示例 1:
输入: [[1,1],2,[1,1]]
输出: [1,1,2,1,1]
解释: 通过重复调用 next 直到 hasNext 返回false,next 返回的元素的顺序应该是: [1,1,2,1,1]。
示例 2:
输入: [1,[4,[6]]]
输出: [1,4,6]
解释: 通过重复调用 next 直到 hasNext 返回false,next 返回的元素的顺序应该是: [1,4,6]。
看看说明:
# """
# This is the interface that allows for creating nested lists.
# You should not implement it, or speculate about its implementation
# """
#class NestedInteger(object):
# def isInteger(self):
# """
# @return True if this NestedInteger holds a single integer, rather than a nested list.
# :rtype bool
# """
#
# def getInteger(self):
# """
# @return the single integer that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a single integer
# Return None if this NestedInteger holds a nested list
# :rtype int
# """
#
# def getList(self):
# """
# @return the nested list that this NestedInteger holds, if it holds a nested list
# Return None if this NestedInteger holds a single integer
# :rtype List[NestedInteger]
# """
class NestedIterator(object):
def __init__(self, nestedList):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
:type nestedList: List[NestedInteger]
"""
def next(self):
"""
:rtype: int
"""
def hasNext(self):
"""
:rtype: bool
"""
# Your NestedIterator object will be instantiated and called as such:
# i, v = NestedIterator(nestedList), []
# while i.hasNext(): v.append(i.next())思路
方法思考一
由于列表的深度不确定,故而也就不能简单的考虑循环来解决。
在二叉树的遍历过程中也是类似的,不能简单的确定末节点,但是其遍历却很简单,也就是只考虑单步,而将问题用栈的数据结构来细化。
这里也可以使用栈来解决问题。不妨来个案例,看看示意图: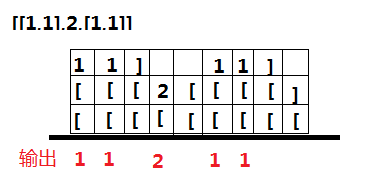
结合提示,调用需要用i.hasNext()判断循环是否继续,用i.next()来取元素。
故而我们可以初始化一个栈,由于hasNext()一次,就要next()取值一次,故而不能简单的用栈空来判断。但是前提是把列表转换成字符串。转换的方式如下:
a = [str(i) for i in [[2,[-1],-3],[-4,-1],-2,-1,-5,-4]]
print("["+",".join(a)+"]")简单思考不难发现,这种方式只适用于小规模数据,如果是大量数据,转换成字符串的操作已经是相当耗时的操作了,得不偿失。
方法思考二
不妨就来适用列表的特性,传入的列表的数据类型是:List[NestedInteger]
故而,我们需要使用到NestedInteger这个类提供的三个方法:getList():return List[NestedInteger]getInteger():return intisInteger():return bool
我没有思考出来,然后百度了一下。看了看。
就是将列表中所有的元素用递归的方式提取元素,然后装载在队列中,然后在next和hasNext中就是元素出队问题。代码如下:
class NestedIterator(object):
def __init__(self, nestedList):
"""
Initialize your data structure here.
:type nestedList: List[NestedInteger]
"""
self.vecotr = []
self.load(nestedList)
def load(self, nestedList):
for i in nestedList:
if i.isInteger():
self.vecotr.append(i.getInteger())
else:
self.load(i.getList())
def next(self):
"""
:rtype: int
"""
front = self.vecotr[0]
self.vecotr.remove(front)
return front
def hasNext(self):
"""
:rtype: bool
"""
return len(self.vecotr) != 0结果:
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-nested-list-iterator




